To read the article on the 0 and 1st conditionals in English please click on this link.
Conditionals
What are conditionals?
Conditionals are sentences that usually begin with ‘IF’.
We use them to talk about different possibilities ‘IF’ something happens or happened.
There are 4 main types of conditionals in English, as well as the mixed conditionals. These 4 types are the:
0 conditional
1st conditional
2nd conditional
and
3rd conditional

The 0 conditional is for something which is always true.
The first conditional is for something which is either likely or possible.
The second conditional is for something which unlikely or impossible.
The third conditional is for something which is for something impossible, because it’s about the past.
Look at this arrow of probability.

Can you see how conditionals go with this arrow?
0, 1st, 2nd and 3rd are all related to their level of probability, with 0 being always true all the way to 3rd which is totally impossible.
Each conditional has two parts.
These parts are called ‘clauses’
A clause is a part of a sentence.
The two clauses in each conditional are the ‘IF’ clause and the ‘MAIN’ clause.

The first conditional
The first conditional is the most important conditional in the English language because it’s the one you need for real everyday life and to discuss possibilities.
It is used to talk about real possibilities or situations.
The structure is, IF + PRESENT + FUTURE
Example:
‘If it is sunny tomorrow, I will go out.”
The ‘is’ is present tense, ‘will go‘ is future tense.
“If I have enough money, I will buy the shirt.”
“have is present tense, “will buy” is future tense.
“If I see the teacher this afternoon, I will give him the homework”.
‘See’ is present tense, ‘will give’ is future tense.
Remember we can also swap the clauses, so we can say:
“If is sunny tomorrow, I will go out.”
or
“I will go out, if it is sunny tomorrow.”
“If I have enough money, I will buy the shirt.”
or
“I will buy the shirt, if I have enough money.”
We can also use the 1st conditional with modal verbs.
So, for example, if + present + MODAL verb.
“If it is sunny tomorrow, I may go out.”
“If it is sunny tomorrow, I might go out.”
May and might are both modal verbs.
We can also use the 1st conditional with imperative verbs.
So, for example, if + present + IMPERATIVE verb.
“If you go to the shop, buy me a sandwich please.”
buy is an imperative verb.
“If you see Peter, give him the book.”
‘Give’ is an imperative verb.
The second conditional
We use the second conditional to talk about something which is very unlikely or impossible to happen. We often use it for things which are imaginary or hypothetical.
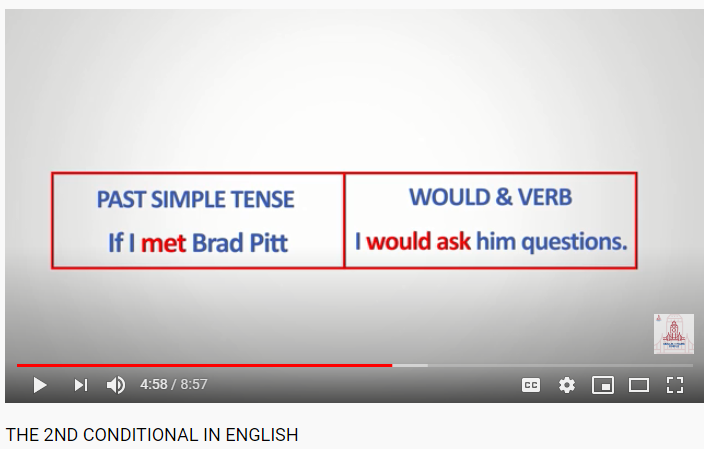
The structure is: IF + PAST TENSE + WOULD & verb.
For example, “If I met Brad Pitt, I would ask him questions.”
It is possible to meet Brad Pitt but very unlikely.
In the if clause “met” is in the past simple tense, and in the main clause there is “would ask” that is would & verb.
IMPOSSIBLE 2nd CONDITIONALS
Now an example of something which is not unlikely but actually impossible.
“If I had wings like a bird, I would fly to Brazil.”
This is impossible and totally imaginary.
“had” wings is in the past simple tense and, “would fly” is would & verb.
Some more examples.
“If I had $50 million, I would build a super-big hospital to help people.”
“If I could be an animal, I would like to be a cat.”
You can also swap these clauses.
So you can say.
“If I had $50 million, I would build a super-big hospital to help people.”
or
” I would build a super-big hospital to help people, if I had $50 million ”
or
“If I could be an animal, I would like to be a cat.”
or
” I would like to be a cat, “If I could be an animal”
We can also replace “would” with “could” so we can say.
“If I had millions of dollars, I could buy many houses.”
or
“If I spoke English very well, I could get a good job.”
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE FIRST AND SECOND CONDITIONALS
- The 1st conditional is used for real life situations and actual possibilities, the 2nd conditional is for imaginary situations.
- The 1st conditional structure is: If + present simple + future but the 2nd conditional is: ‘If + past simple + would & verb’.
You can also watch this video for more information.



Thanks for the explanation. It is very useful.
Could you also make a post about using ‘ be to+verb ‘ in conditional sentences?